Benign Prostatic Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, BPH)
What is benign prostatic enlargement?
Prostateis the glandular tissue that is responsible for the sexual life of men and contributes to the formation of semen with the secretion it produces. In men, it is located at the exit of the urinary bladder and passes through the urethra, which we call the urethra. It is an organ that grows with the effect of various hormones with aging. This growth compresses the urinary canal passing through the prostate and causes various complaints by closing the bladder outlet with the mass effect.
What types of complaints does it cause?
Waking up to urinate during the night and needing to urinate frequently during the day are common symptoms. There may also be a decrease in urine velocity. There may be waiting and difficulty in starting to urinate, and there may still be a drop of urine after urination. In addition, the person may feel that the bladder is not completely empty after urinating.
What types of treatment options are there?
Patients who have problems with urination are treated with medication or surgical methods. The first step in treatment should be drug therapy. In drug treatment, drugs that relax the muscles in the prostate and facilitate urine flow (alpha-blocker drugs) and drugs that cause a decrease in the volume of the prostate (drugs that inhibit 5-alpha reductase) are used.
In which cases is surgical treatment chosen in the treatment of BPH?
Surgical treatment can be applied to patients who must use drugs due to prostate enlargement, but do not respond to treatment or for whom the drug becomes insufficient over time, and patients who cannot use drugs due to side effects. In addition, surgical treatment should be planned for patients who have stones in their bladder due to prostate enlargement, who have recurrent bleeding in their urine, who have frequent urinary tract infections, and who need to have a catheter inserted due to not being able to urinate at all. The patient's age, medications, additional diseases, and prostate size are considered in determining which method to choose surgically.
Which surgical treatments are available in the surgical treatment of the prostate?
In surgical treatment, it is technically aimed at removing the enlarged tissue. There are some classical methods (transurethral resection of the prostate and open prostatectomy) and more recently laser methods and robotic methods for the surgical treatment of prostate enlargement.
Which endoscopic method is more effective in the treatment of BPH?
All methods other than open removal of the prostate are called endoscopic methods. These methods developed for the treatment of BPH have not shown any remarkable differences in terms of treatment efficacy to date. The generally accepted view is that these methods have similar efficacy and that their side effects are at an acceptable level. The best alternatives in these, in order of activity.
- Transurethral resection (TUR): applied with bipolar, monopolar or plasmakinetic energy.
- Laser vaporization: It is applied with KTP, diode, thulium laser.
- Laser enucleation: HoLEP method applied with holmium laser, ThuLEP method applied with thulium laser.
- Robotic transvesical simple prostatectomy
- Water vapor therapy
What is open prostatectomy, in which cases is it performed?
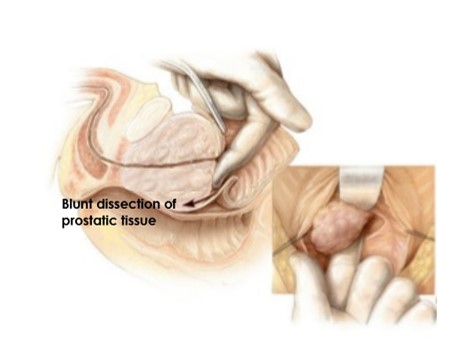
It is a type of surgery performed by incision made on the lower part of the abdomen in large prostates and by opening the bladder and using the surgeon's fingers(figure 1). It is suitable in cases over 80 grams, if there are stones or diverticulum in the bladder together. However, in this method, scars from open surgery remain on the body. The patient stays in the hospital longer and the catheter time is longer. Serious bleeding may develop. The risk of retrograde ejaculation, which is the backward flow of sperm, is high. There is a risk of developing stenosis in the urethra and bladder neck.
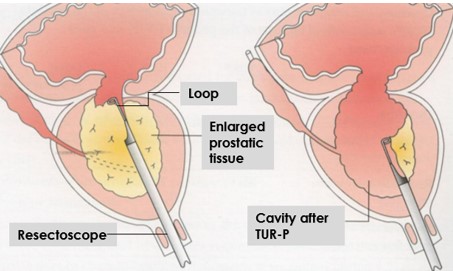
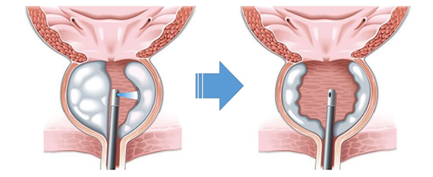
What is transurethral resection of the prostate (TUR-P)?
It is the standard surgical treatment of BPH. This procedure is done by entering the urethra, which we call the external urinary canal, without making an incision in the lower abdomen, and using a resectoscope. There is a loop of wire at the end of the resectoscope, and when high-frequency electricity is passed through this ring, it cuts the prostate into small pieces (figure 2). camera on the resectoscope also allows the doctor to monitor the field with a high-quality image on a video screen. The cut pieces are taken out of the resectoscope. Today, this method is generally applied in prostates weighing between 30 and 80 grams. The procedure is safe and very common. Hospital stay is short. However, there is a low risk of urinary incontinence with bleeding, retrograde ejaculation, urethral stricture.
What is a transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP)?
It is a method used in men with a prostate smaller than 35 ml and without severe prostate enlargement. It can be applied to men who cannot tolerate drug therapy. An incision is made from the bladder neck to the prostate with a different-tipped loop placed on the resectoscope (figure 3). A catheter is placed in the bladder to ensure urine flow after the procedure.
What is laser vaporization of the prostate?
It is one of the most used treatments. For this purpose, different laser systems such as KTP, diode, thulium laser can be used. The laser is advanced through the resectoscope into the enlarged prostate tissue. During the procedure with the laser, a small part of the prostate is heated and the prostate tissue, which reaches the boiling point, begins to evaporate. Then the same process is applied to the other parts (figure 4). Since the heat from the laser seals the blood vessels during the procedure, bleeding is less during the procedure. It can be used in patients who use blood thinners due to other diseases and whose prostate is less than 80 ml. A catheter is placed in the bladder to allow urine flow after surgery. It provides rapid improvement in urine flow,short hospital stays and catheter time. It has disadvantages such as its low effectiveness in large prostates, the need for other procedures over time as the prostate continues to grow, and the inability to perform pathological examination because the prostate tissue is vaporized during the procedure.
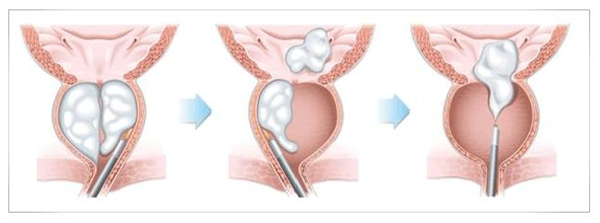
What is laser enucleation of the prostate?
With the endoscope, the enlarged prostate area is entered through the urinary canal, and the area between the enlarged prostate tissue (adenoma) and the prostate capsule is entered with the help of laser, and the enlarged prostate adenoma is peeled from its capsule in several pieces according to its size and thrown into the bladder. This stripping process is called enucleation (figure 5). These adenoma tissues in the bladder are made into minced meat with a device called a morcellator, and these small pieces are taken out and sent for pathological examination. A catheter is placed in the bladder to allow urine flow after surgery. It is generally suitable for prostates over 80 ml. It is also a good option for smaller prostates. It is also a good alternative for men who use anticoagulant. It provides rapid improvement in urine flow, short hospital stay and catheter time. However, in small prostates, the procedure may take longer. There is also the risk of retrograde ejaculation.
What is HoLEP surgery?
It is laser enucleation of the prostate with a holmium laser (figure 6). HoLEP; It is an abbreviation for Holmium Laser Enucleation Prostate. The widespread use of laser technology in the urology department paved the way for HoLEP technology. Prostate enlargement surgery performed with HoLEP technology is an operation in which spinal anesthesia (anesthetizing from the waist down) is considered sufficient. In the HoLEP operation, all the tissue of the prostate except the capsule is removed, and no growth occurs in the remaining tissue. The removed diseased tissue is then pathologically examined, and it is investigated whether this tissue is cancerous tissue. In surgeries where laser treatment is applied, the patient loses less blood thanks to the laser's ability to control bleeding. In addition, HoLEP technology is a method that can be used with peace of mind for those who use anticoagulant. Prostate enlargement treatment with HoLEP technology is increasing its popularity day by day due to the positive results it has given so far.

What is ThuLEP surgery?
Laser enucleation of the prostate with a thulium laser (figure 7).ThuLEP;It is an abbreviation for ThuliumLaser Enucleation Prostate. In fact, although the operations performed with holmium and thulium laser are named differently, the purpose of both is to strip the prostate from the capsule (enucleation). Holmium laser is used during HoLEP surgery, and thulium laser is used in ThuLEP surgery. The latest in laser technology is the thulium laser. The thulium laser has a more bleeding-stopping and cutting effect than the holmium laser. It is used in prostate enlargement, in the treatment of bladder and upper urinary tract tumors and stones. This laser technology allows the removal of healthy and cancerous tissues as a whole and a healthier pathological examination. ThuLEP is a surgical method that can be applied to anyone who is recommended prostate surgery. Although the classical TUR method is not recommended for prostates larger than 80-100gr, ThuLEP can be applied much more successfully, especially for large prostates. In addition, there is no upper limit on prostate size for ThuLEP. It is also successfully applied in the same session in patients with bladder stones accompanying prostate enlargement. It can be applied more safely than other techniques in patients using anticoagulant.
How is a robot used in the treatment of BPH?
In BPH, robot is a new surgical method that provides complete removal of prostate tissue and gives results similar to open surgery. Here, the robot is used differently from the technique used to remove cancerous tissue in prostate cancer, but the number and placement of robot arms in the technique used in prostate cancer are similar. Technically, unlike prostate cancer, here the bladder is opened first. The prostate is reached through the bladder neck and the capsule is left and the enlarged tissues of the prostate are removed in one piece, which is called robotic transvesical simple prostatectomy. In appearance, it is almost like leaving the peel of a tangerine and removing the inside. You can find more information about the use of robots in the treatment of BPH in the "Robotic Urology-Robotic Surgery in Adults-Robot in Benign Prostatic Enlargement" section of this site.
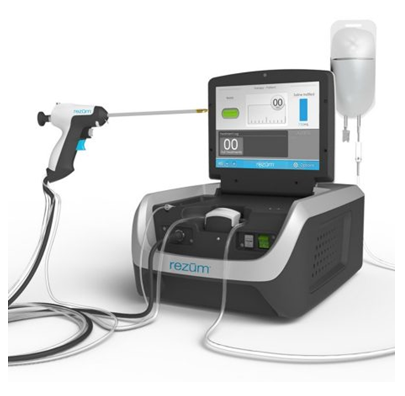
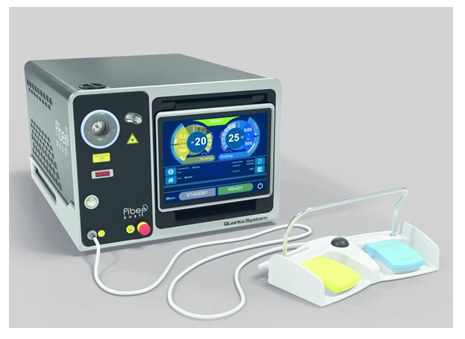
What is water vapor therapy (Rezum) for the prostate and how is it applied?
An optical system is entered into the urinary canal with a special device from the tip of the penis. Enlarged prostate tissues are reached under direct vision. The needle protruding from the tip of the handpiece special for the Rezum method is inserted into the enlarged area and the hot water vapor created by using radio frequency current is injected into the depths of the tissue. Depending on the enlargement characteristics of the tissue, the application is made to the right, left and, if necessary, the middle regions of the prostate. Each application is completed in 9 seconds. The Rezum system ensures that the heat effect in the form of water vapor is delivered into the growing prostate tissue (picture 8). Thanks to the condensed water vapor in the tissue, the heat effect breaks the membranes of the benign proliferating prostate gland cells. Thus, in addition to providing cell death, the vessels are blocked, and nerve cells defined as alpha adrenergic are rendered inoperable. Cells that lose their vitality are eliminated over time by using the body's natural systems.
The therapeutic process that occurs with the application of Rezum becomes more and more evident over time, and the obstruction at the bladder outlet disappears, and the urine flow becomes easier. Rezum treatment system is different from other closed surgical methods; It does not require deep anesthesia, does not need to stay in the hospital, does not cause bleeding during the surgical procedure, does not require absolute bladder washing from the catheter after the application, can be used safely in patients using cardiac and brain pacemakers, and the risk of semen retraction after the treatment is very low (5%) It has plus features such as less than .